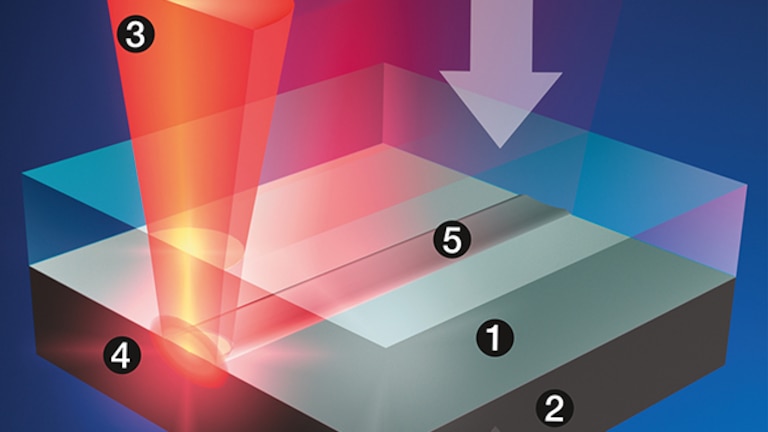
Beratung Lasertechnologie
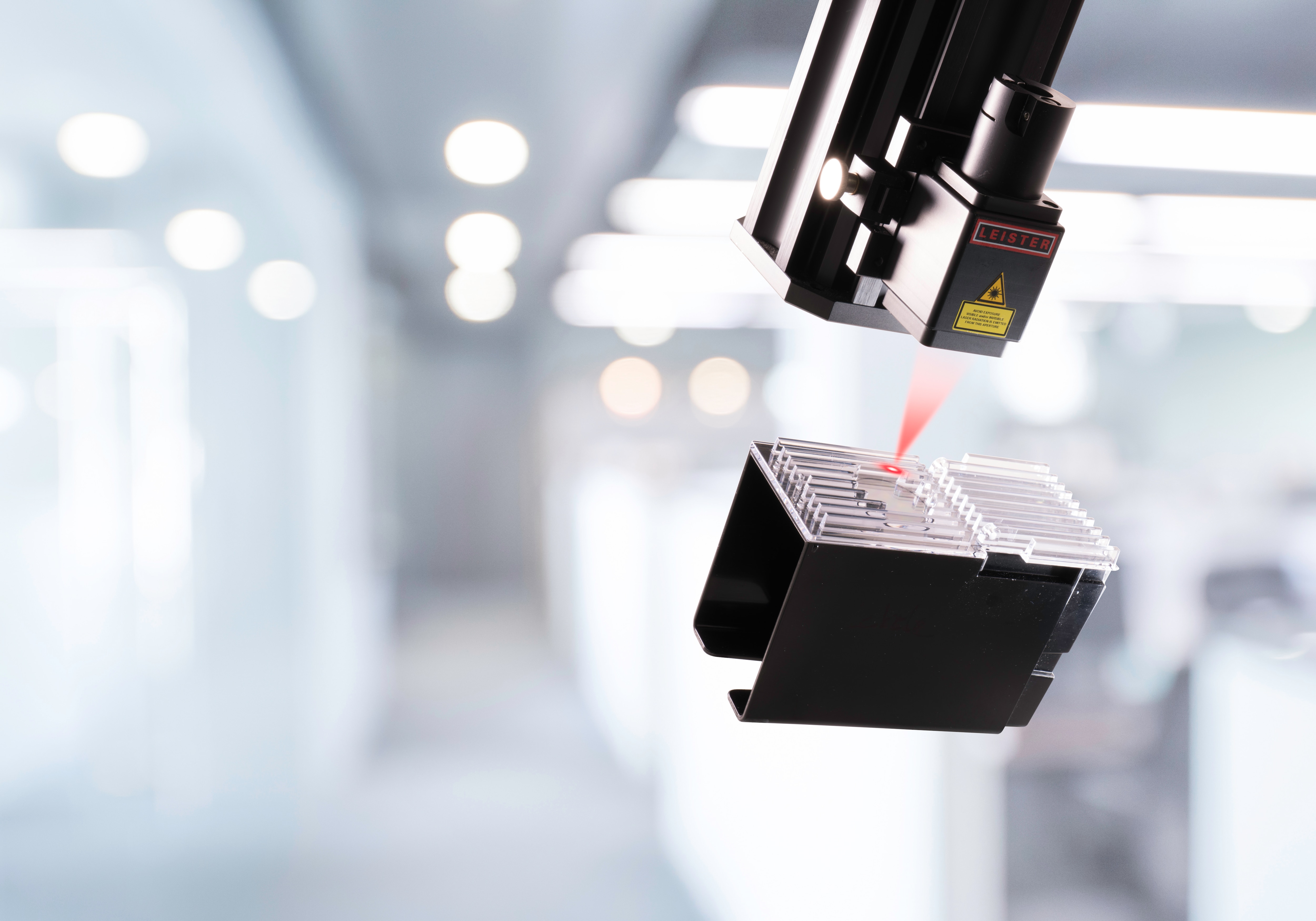

Wir unterstützen Sie dabei, das Laserschweissen von Kunststoffen in Ihrem Unternehmen zu etablieren. Das bedeutet für Sie, dass wir Sie in der Gestaltung Ihrer Applikation rundum beraten – vom Design über das optimale Schweissverfahren bis hin zur Maschineninstallation.
Applikationslabor für Laserprozess- und Materialtests
Leihgeräte für eigene Tests oder als temporäre Lösung
Unterstützung bei der Konstruktion und Auswahl der geeigneten Fügegeometrie
Service im Überblick
Unser Customer Support bietet Ihnen verschiedene Dienstleistungen, damit Sie Ihre Laserschweisssysteme langfristig, kostengünstig und effizient betreiben können. Um möglichst allen Kundenbedürfnissen gerecht zu werden, sind unsere Dienstleistungen modular aufgebaut.
Diese Dienstleistungen fokussieren sich auf die Aufrechterhaltung des Betriebes und die Minimierung des Produktionsausfalles:
- Montage, Inbetriebnahme beim Kunden
- Helpdesk für telefonische Unterstützung bei Störungen über (1st Level Support)
- technische Unterstützung für detailliertere Analysen (2nd Level Support) mit R&D (3rd Level Support)
- Entsendung eines Servicetechnikers
- Remote-Zugriff für Ferndiagnose und Korrekturen
- Express-Lieferung von Ersatzteilen
- Reparaturen
- präventive Wartung, Inspektion, Kalibrierung
- generelle Überholung und Modernisierung des Systems, Update und Upgrade von Komponenten
- Austauschdienst für gebrauchte Teile
- Produktionsunterstützung bei Problemen im Betrieb, nach Inbetriebnahme oder bei neuem Betreiber
Damit Sie mit unseren Systemen effizient produzieren können, unterstützen wir Sie mit folgenden Dienstleistungen:
- Wartungsverträge mit definierten Dienstleistungen und Reaktionszeiten
- Schulungen zum Vermitteln von Theorie- und Praxiswissen über Betrieb, Unterhalt, Einrichtung, Kalibrierung, Ersatzteile, usw.
- Vorschlag eines individuellen Basispaketes an Ersatzteilen für Neuanlagen, damit alles Notwendige kurzfristig verfügbar ist
- Übernahme aller Tätigkeiten bei Maschinenumzügen – vom Herunterfahren bis zur Wiederinbetriebnahme
Dienstleistungen